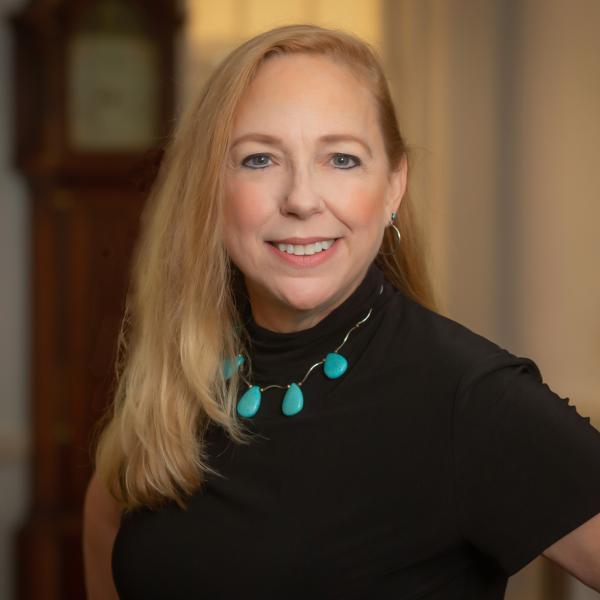
Karen M. Schmidt
Professor of Psychology, General Faculty| Director of +1MA Advising
924-0694
226A Gilmer Hall

Research Areas:
I am interested in examining the latent structure of complex abilities across the lifespan; personality, pain, and the relationship between personality and pain; Methodological investigations center around item response theory models for understanding change and processing components in abilities. Longitudinal analyses of item level variables are critical and important issues in investigating developmental and psychometric properties of psychological batteries, survey questionnaires, and inventories.
Publications
- Bowles, R. P., Schmidt, K. M., Kline, T. L., & Grimm, K. J. (In Press). Ben Wright, Rasch measurement, and cognitive psychology. Manuscript submitted to M. Wilson & G. Englehard (Eds.), Conference proceedings from a Festschrift in honor of Ben Wright.
- Erbacher, M. K., Schmidt, K. M., & Bergeman, C. (under review). Relationships among longitudinal measurements of positive and negative affect in later life: An idiographic approach using derivatives.
- Cox, D. J., Ford, D., Schmidt, K. Singh, H. & Gonder-Frederick, L. (under review). Screening for Drivers at High Risk for Driving Mishaps.
- Singh, H., Gonder-Frederick, L.,Schmidt, K., Ford, D., Hawley,J., & Cox, D. J. (under review). Avoidance of Hyperglycemia in People with Type 1 Diabetes.
- Gonder-Frederick, L. A., Vajda, K. A., Schmidt, K. M., Cox, D. J., DeVries, H., Ozgul, E., Kanc, K., Schächinger, H., & Snoek, F. J. (2013). Examining the Behaviour subscale of the Hypoglycaemia Fear Survey: An international study. Diabetic Medicine, 30 (5):603-609.
- Schmidt, K. M., & Embretson, S. E. (2012). Item response theory and measuring abilities. In J. A. Schinka and W. F. Velicer (Eds.), Research Methods in Psychology (2nd ed.). Volume 2 of Handbook of Psychology (I. B. Weiner, Editor-in-Chief). NY: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- Lick, D. J., Patterson, C. J., & Schmidt, K. M. (2013). Recalled social experiences and current psychological adjustment among adults reared by lesbian and gay parents. Journal of GLBT Family Studies, 9, 230–253.
- Erbacher, M. K., Schmidt, K. M., Boker, S. M., & Bergeman, C. (2012). Measuring positive and negative affect in older adults over 56 days: Comparing trait level scoring methods using the Partial Credit Model. Journal of Applied Measurement,13,146-164.
- Lick, D. J., Tornello, S. L., Riskind, R. G., Schmidt, K. M., & Patterson, C. J. (2012). Social climate for sexual minorities predicts well-being among heterosexual offspring of lesbian and gay parents. Sexual Research and Social Policy, 9, 99-112.
- Gonder-Frederick. L. A., Schmidt, K. M., Vajda, K. A., Greear, M. L., Singh, H., Shepard, J. A., & Cox, D. J. (2011). Psychometric Properties of the Hypoglycemia Fear Survey-II for Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care, 34, 801-806.
- Lick, D. J., Schmidt, K. M., & Patterson, C. J. (2011). The Rainbow Families Scale (RFS): A measure of experiences among individuals with lesbian and gay parents. Journal of Applied Measurement, 12, 222-241.
- Chambers, A. L., Schmidt, K. M., & Wilson, M. N. (2006). Describing differences among a sample of low income fathers: A glimpse into their romantic relationships. Psychology of Men and Masculinity, 7, 144-152.
- Kline, T. L., Schmidt, K. M., & Bowles, R. P. (2006). Using LinLog and FACETS to model item components in the LLTM. Journal of Applied Measurement, 7, 74-91.
- Williams, M. T., Turkheimer, E., Schmidt, K. & Oltmanns, T. (2005). Ethnic identification biases responses to the Padua Inventory for obsessive-compulsive disorder. Assessment, 12,174- 185.
- Kline, T. L., & Schmidt, K. M. (2005). Rasch analysis explicating processing mechanisms of The Object Location Memory Test. Journal of Applied Measurement, 6,382-395.
- Schmidt, K. M. (2004). Item generation: Difficult questions made easier. [Review of the book: Item generation for test development (Irvine, S. H., & Kyllonen, P. C., (Eds.). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum. Contemporary Psychology, 49, 577-579].
- Schmidt, K.M., Llewellyn, P. L., Taylor, G. J., Weber, P.G., Hong, B., Sellers, R., Wise, C., Wolak, C., McGaw, L, & Nielson, S. (2003). Cloninger’s Temperament and Character Inventory correlates with personality characteristics of organ donation advocates. Journal of Clinical Psychology in Medical Settings, 10, 173-185
- Schmidt, K. M., & Embretson, S. E. (2003). Item response theory and measuring abilities. In J. A. Schinka and W. F. Velicer (Eds.), Research Methods in Psychology (Pp.429-445). Volume 2 of Handbook of Psychology (I. B. Weiner, Editor-in-Chief). NY: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- Schmidt, K. M. (2003). How should we score our tests? [Review of the book: Test scoring (Thissen, D, and Wainer, H., (Eds.). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum. Contemporary Psychology, 48, 374-377].
- Embretson, S. E., & Schmidt McCollam, K. M. (2000). Psychometric approaches to understanding and measuring intelligence. In R. J. Sternberg (Ed.). Handbook of Human Intelligence. (Pp. 423-444). NY: Cambridge University Press.
- Embretson, S. E., & Schmidt McCollam, K. M. (2000). A multicomponent Rasch model for measuring covert processes: Application to lifespan ability changes. In M. Wilson & G. Engelhard, (Eds.), Objective measurement: Theory into practice (Vol. 5) (Pp. 203-218). NJ: Ablex.
- Nesselroade, J. R., & Schmidt McCollam, K. M. (2000). Putting the process in developmental processes. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 24, 295-300.
- Green, S. B., Hershberger, S. H., Marquis, J., Thompson, M., & McCollam, K. (1999). The overparameterized analysis of variance model. Psychological Methods, 4, 214-233.
- McCollam, K. M. (1998). [Review of the book Models for uncertainty in educational testing]. Structural Equation Modeling,5, 310-312.
- McCollam, K. M. Schmidt (1998). Latent trait and latent class models. In G. M. Marcoulides, (Ed.), Modern methods for business research (Pp. 23-46). NJ: Erlbaum.
- McCollam, K. M., Embretson, S. E., Mitchell, D. W., & Horowitz, F. D. (1997). Using confirmatory factor analysis to identify newborn behavior structures of the NBAS. Infant Behavior and Development, 20, 123-131.
- McCollam, K. M., Embretson, S. E., Horowitz, F. D., & Mitchell, D. W. (1996). Scoring the NBAS: To recode or not to recode. Infant Behavior and Development, 19, 63- 69.
- Colombo, J., McCollam, K., Coldren, J., Mitchell, D. W., & Rash, S. (1990). Form categorization in 10-month-olds. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 49, 173-188.